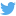Wetlands slow erosion, help recharge groundwater, and help prevent flooding.
Like a ‘giant natural water filter’ these wet, spongy soils trap the sediment and particles in polluted water allowing clean, fresh water to pass through. Because of this unique process, wetlands play a vital role in ensuring the availability of good quality water in large volumes and form part of critical catchments feeding into major water ways and rivers. These vleis provide fresh pastures for livestock, fertile soil for agriculture and critical habitats for wildlife.